WHAT ARE ESG STANDARDS? ?
Sustainable activities are becoming more and more popular in Vietnam. However, ESG standards are still very new, while the three environmental - social - governance aspects of ESG are the focus of sustainable investment. No longer a trend, ESG is now considered the key to strong and long-term development in all fields.
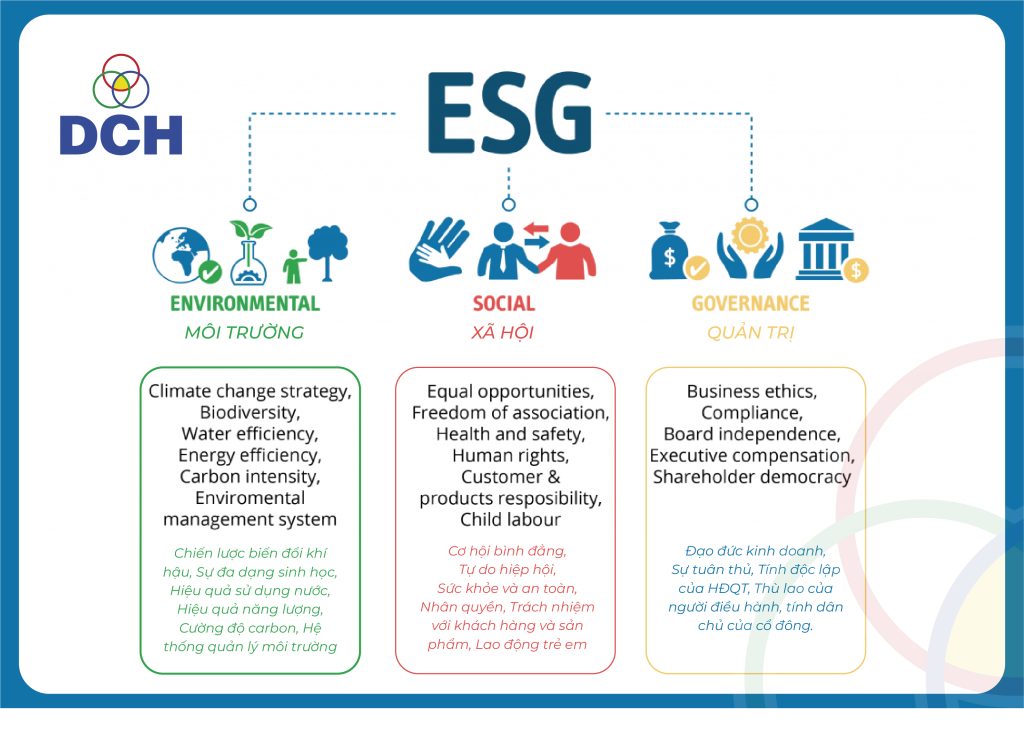
ESG is an acronym for Environment, Social and Governance. This is a set of three standards to measure factors related to the orientation and sustainable development activities of enterprises. ESG helps organizations identify risks and opportunities, as well as the level of impact when applying them to operations.
ESG scores are based on a company's environmental and social impacts and its management performance in managing those impacts. A higher ESG score indicates a brand's good ESG practices.
ESG standards cover a wide range of issues, stemming from international law, local law, or agreements and principles in each country. To implement ESG, businesses need to meet three main focuses with dozens of specific criteria.
ENVIROMENT

The first aspect is E – Environmental, which measures the extent to which a business impacts the environment and natural resources throughout the production, operation, management process... Specifically, the organization will be considered for:
1. Climate Change
The climate change criteria will be assessed based on international and domestic commitments, national policies and local regulations. For Vietnam, at the 2021 United Nations Summit (COP26), Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh impressed with the announcement of commitments on climate change response.
- Aim for a 43.5% reduction in total national emissions by 2030, and net zero carbon emissions by 2050.
- Reduce methane emissions by at least 30% by 2020, 40% by 2030.
With a pioneering role in creating ESG policies, the government will promote Vietnamese businesses with clearer motivation and basis when striving to achieve commitments related to ESG goals.
2. Energy
Enterprises implementing ESG must ensure the exploitation and efficient use of energy resources. In addition to optimization, alternative energies of unlimited nature are encouraged such as solar energy, natural wind, etc. This will help the environment avoid energy depletion, the organization can also operate at all times without depending on limited resources, promoting the production process.
3. Natural resources
Resources here include land, water, trees, minerals, air, etc. To achieve a high ESG score in this category, businesses must ensure that they have all the necessary licensing documents when using any resource. In addition, many organizations also score points when they proactively/contribute to the rehabilitation and restoration of polluted areas.
In particular, instead of minimizing, a part of businesses growing in the 4.0 era also researches and deploys new technologies that can create their own resources, without any impact on the environment.
4. Waste treatment and recycling
To handle waste according to ESG standards, businesses need to compile a detailed list of types and quantities of hazardous waste. Then collect, classify them and store them in a separate place to ensure they do not cause pollution. Based on policies, organizations can move and bring them to appropriate licensed treatment facilities. If possible, companies can recycle and reuse to reduce waste to the environment and optimize energy.
Businesses can invent by their own, or use recycling services to ensure that waste is properly disposed of. Some substances have ratios and specifications that are, or even regulated by law.
SOCIAL

The second aspect of ESG is Social, which helps businesses evaluate social factors such as the company's business relationships with customers and partners; working conditions of employees, also known as Labor Law in Vietnam.
1. Privacy and Security
Although it is an important criterion, the regulations and laws on them are still quite new in our country. The current privacy law in Vietnam is applied based on the Civil Code, Cyber Security, Information Technology...
To implement ESG, businesses need permission from owners before collecting, using or doing anything with their data. In particular, they must absolutely not disclose personal information, and must commit to data protection measures.
2. Diversity, equity and inclusion
The Labor Law will be the basis for assessing the ESG score in this section. According to the law, organizations cannot discriminate against employees regardless of their gender, skin color, race, religion, or social class or organization. Male and female employees need to be equal in all aspects: work, promotion opportunities, salary, etc.
3. Safe working environment
The workplace must ensure occupational safety and health. ESG strictly prohibits forced labor, abuse, exploitation, harassment, etc. Of course, the standards are also strict in the use of human resources under 18 years old, the organization must perform on time as well as the nature of the work permitted by the Labor Law.
4. Working conditions
ESG will base on the regulations in Vietnamese law to consider the score for businesses such as salary, working hours, health check, insurance policy...
GOVERNANCE

The final aspect of ESG is Governance, a group of assessments that look at an organization's operations to ensure efficiency, transparency, business ethics, and compliance with local regulations.
1. ESG reporting disclosure
Vietnamese law requires businesses implementing ESG to publicly disclose information and annual operating results such as resource exploitation and consumption, labor policies, financial reports, contributions to the community, etc. This report must be submitted to the State Securities Commission of Vietnam and the Stock Exchange publicly.
2. Anti-bribery and corruption
This is a very important factor in management, and will be evaluated according to the Law on Anti-Bribery & Corruption - Criminal Law of Vietnam.
3. Board diversity and inclusion
This ESG criterion assesses the diversity of board members in terms of gender and background. Under Vietnamese law, in some cases, an independent board is also required, for example, 1/5 of the board members of an unlisted public company must be independent.
Above is a list of criteria that businesses need to meet when implementing ESG. To keep up with the trend and successfully complete this set of standards, leaders need to have a deep understanding of ESG and how to properly manage current legal frameworks and ESG practices.
WHY APPLY ESG STANDARDS?

1. Consumer requirements
The World Economic Forum's report "The Future of Consumption in Fast-Growth Markets: ASEAN" published in June 2020 showed that 80% of consumers in the ASEAN region are concerned about sustainability and have changed their living habits to become more environmentally friendly (Moore, 2022).
The latest data from the Edelman Trust Barometer (2022) report shows that how businesses treat employees and suppliers has and is influencing consumer purchasing behavior. Accordingly, 1/3 of consumers have stopped using a brand that they perceived did not behave appropriately in response to the crisis; 71% said that if they perceived a brand as putting profits before people, they would never trust that brand again.
2.Investor requirements
Consumer expectations have changed the way investors approach investing in recent times. The 2022 Global ESG Standards Study shows that ESG is becoming an increasingly important criterion in the eyes of global investors. As of 2022, nearly 90% of investment institutions considered ESG criteria before making investment decisions.
When asked about the importance of ESG to their investment approach in 2022, more than a quarter of global investors said ESG was “central” to their investment approach (26% vs. 28% in 2021). However, a higher proportion expressed their opinion of ESG investing as “accepting” (34% vs. 32%) and “adhering” (29% vs. 24%).
Overall, Europe is the world's leading region in ESG investing with 93% (compared to 79% in North America, 88% in Asia-Pacific). Of which, 31% of European investors put ESG at the heart of their investment approach (compared to 18% in North America, 22% in Asia-Pacific). This shows that Europe's investment market and legal framework are more mature. In contrast, North America is the least confident and applies ESG in investment.
In addition, ESG is increasingly asserting its position in the investment community as research shows that only 13% of global investors agree that ESG is a short-term and temporary movement. This shows that most investors see ESG as an inevitable trend in the long-term investment context.
(Source: https://isokna.com.vn and https://aitcv.ac.vn)
